The protection of intellectual property is considered essential for business growth in Nepal. Local Trademark Registration in Nepal is governed by specific legal frameworks to ensure that brand identity is secured. When a trademark is registered, exclusive rights are granted to the owner within the jurisdiction of Nepal. This blog provides a detailed, factual, and legal analysis of how trademark registration Nepal is conducted, the costs involved, and the procedural steps required by the Department of Industry.
The Legal Framework for Trademark Registration in Nepal
The process of Local Trademark Registration in Nepal is administered by the Department of Industry (DOI), which operates under the Ministry of Industry, Commerce, and Supplies. The primary legislation that regulates this process is the Patent, Design and Trademark Act, 2022 (1965). Furthermore, the Patent, Design and Trademark Rules, 2022 are implemented to guide the procedural aspects.
Under these laws, a trademark is defined as any word, symbol, logo, device, label, or combination thereof that is used to distinguish goods and services. It is noted that Nepal is a party to the Paris Convention for the Protection of Industrial Property and the TRIPS Agreement. Consequently, priority claims from member countries are recognized if the application is filed within six months of the initial filing date.
Why is Local Trademark Registration in Nepal Essential?
For businesses operating in Nepali markets, Local Trademark Registration in Nepal is not merely a formality; it is a necessity. Several benefits are afforded to the owner of a registered mark:
- Exclusive Rights: The use of the trademark is restricted to the registered owner. Unauthorized use is prohibited.
- Legal Protection: Legal action can be taken against infringement.
- Asset Creation: The trademark is recognized as an intangible asset. Value is added to the business.
- Consumer Trust: Brand loyalty is established, and consumer confidence is built.
Step-by-Step Process for Local Trademark Registration in Nepal
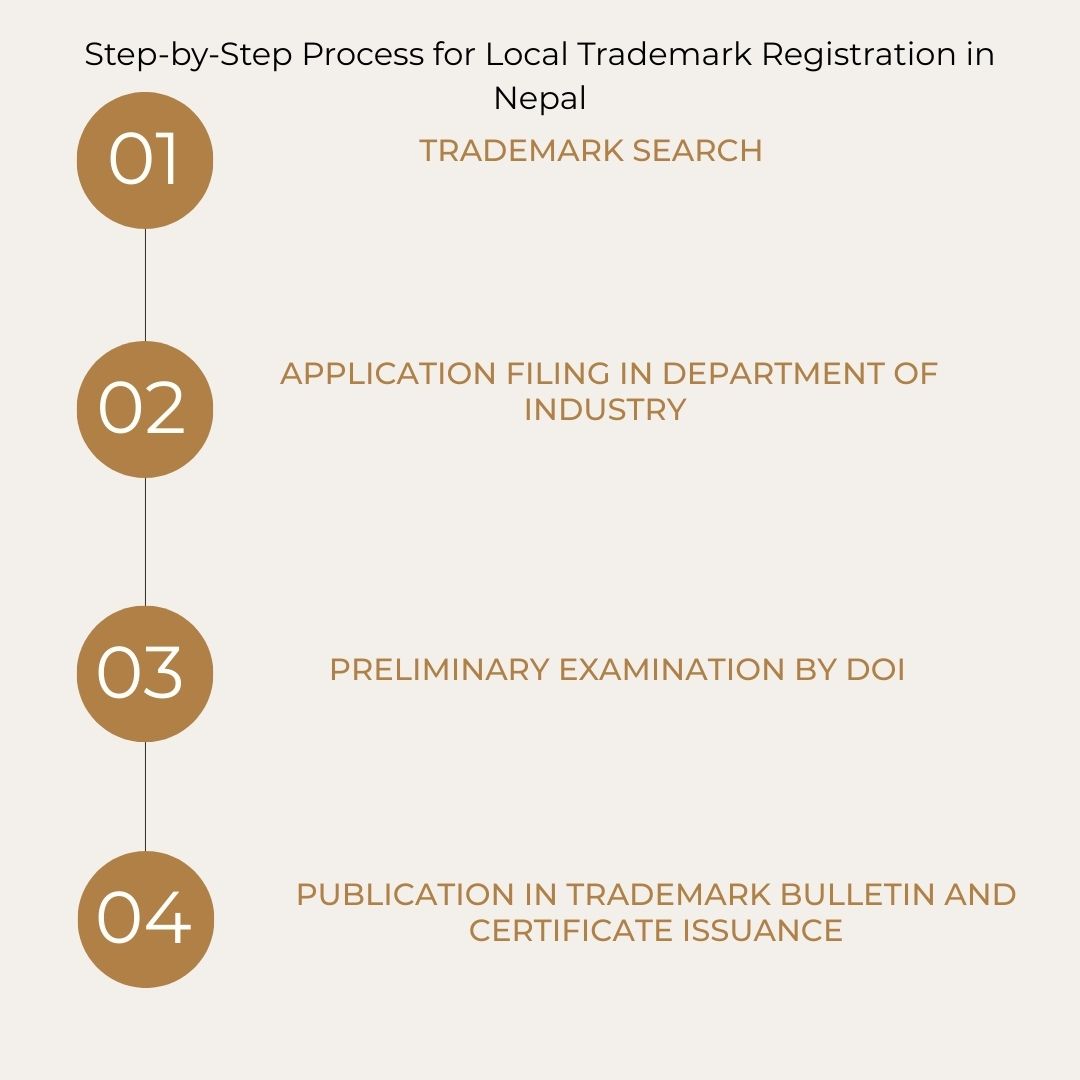
The procedure for registering a trademark is systematic. To ensure high readability and clarity, the steps are outlined below:
|
Step |
Action |
Description |
|
1 |
Trademark Search |
A preliminary search is conducted at the DOI to ensure the mark is unique. |
|
2 |
Application Filing |
The application is submitted to the Patent, Design, and Trademark Section. |
|
3 |
Preliminary Examination |
The application is examined by the registrar for compliance and distinctiveness. |
|
4 |
Publication |
If approved, the mark is published in the Industrial Property Bulletin. |
|
5 |
Opposition Period |
A 35-day window is provided for third parties to file oppositions. |
|
6 |
Registration & Certificate |
If no opposition is filed, the registration certificate is issued. |
1. Trademark Search
Before an application is filed, a thorough search is recommended. This search is performed to verify that the proposed mark is not identical or similar to an existing registered mark. Conflicts are identified early, and rejection risks are minimized.
2. Filing the Application
An application for Local Trademark Registration in Nepal must be filed using the prescribed form. The following details are included:
- The name and address of the applicant.
- A clear representation of the trademark (logo or word).
- The list of goods and services (classified according to the Nice Classification).
- A power of attorney if the application is filed through an agent.
3. Examination and Publication
Once the application is received, a formal examination is conducted. During this phase, distinctiveness and compliance with the Trademark Act Nepal are assessed. If the application is accepted, it is published in the official Gazette. This publication is done to invite public objections.
4. Registration and Renewal
If no opposition is received within 35 days of publication, the trademark proceeds to registration. A certificate of registration is then issued by the Department of Industry. It is important to note that the registration is valid for an initial period of seven years from the date of filing. Subsequently, the trademark must be renewed every seven years.
Required Documents for Registration
To facilitate the smooth processing of Local Trademark Registration in Nepal, specific documents must be submitted. These documents are verified by the authorities:
- Application Form: Duly filled Form No. 6 (for individuals) or Form No. 7 (for companies).
- Power of Attorney: Authorization for a local representative if the applicant is foreign.
- Trademark Specimen: A soft copy and hard copy of the logo.
- Citizenship/Company Registration: Proof of identity for individuals or company registration for firms.
- Government Fee: A voucher indicating payment of the application fee.
Cost and Fee Structure
The cost of Local Trademark Registration in Nepal is determined by the official schedule of fees. The fees are subject to change based on government policy. The standard fee structure is summarized below:
|
Description |
Fees (NPR) |
|
Application Filing Fee |
NPR 3,000 (Per Class) |
|
Registration Certificate Fee |
NPR 5,000 (Per Class) |
|
Renewal Fee |
NPR 10,000 (Per Class) |
|
Legal/Agent Fees |
Variable (Depends on service provider) |
Note: Additional costs may be incurred if legal services are hired for opposition or hearing proceedings.
Timeline for Registration
The duration required for Local Trademark Registration in Nepal varies. Generally, the process is completed within 6 to 12 months. However, this timeline can be extended if objections are raised or if there are backlogs at the Department of Industry.
- Examination: 1-3 months.
- Publication: Immediate after examination.
- Opposition/Registration: 3-6 months.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
To optimize for "People Also Ask" and Voice Search, the following FAQs regarding Local Trademark Registration in Nepal are provided:
Is Local Trademark Registration in Nepal mandatory?
While registration is not strictly mandatory for trading, it is highly recommended. Without registration, legal protection against infringement is difficult to enforce. Brand security is significantly compromised.
What is the validity of a registered trademark in Nepal?
A trademark is valid for seven years from the date of application. It must be renewed subsequently for additional periods of seven years.
Can a foreigner apply for a trademark in Nepal?
Yes, a foreign entity can apply. However, an application must be filed through a local agent or attorney. A Power of Attorney must be submitted. Additionally, under the Paris Convention, priority can be claimed within six months of the home country filing date.
What are the grounds for trademark refusal in Nepal?
A trademark is refused if it is:
- Descriptive or generic.
- Contrary to public order or morality.
- Identical or confusingly similar to an existing registered mark.
- Identical to a well-known trademark.
How many trademark classes are accepted in Nepal?
Nepal follows the International Classification of Goods and Services (Nice Classification). An application can be filed for one or multiple classes.
What happens if a trademark is not renewed?
If a trademark is not renewed, the protection lapses. The mark becomes available for registration by other parties. However, a grace period of one year is usually allowed for late renewal with a fine.
Conclusion
The process of Local Trademark Registration in Nepal is a strategic legal maneuver for any business. By adhering to the guidelines set by the Patent, Design and Trademark Act 2026, intellectual property is effectively safeguarded. It is advised that professional legal assistance be sought to navigate the complexities of the application and potential opposition phases.
Call to Action: To secure your business identity today, contact our expert legal team for a consultation on Local Trademark Registration in Nepal. Ensure your brand is protected under the full extent of the law.