Understanding Nepal Government Federal Structure
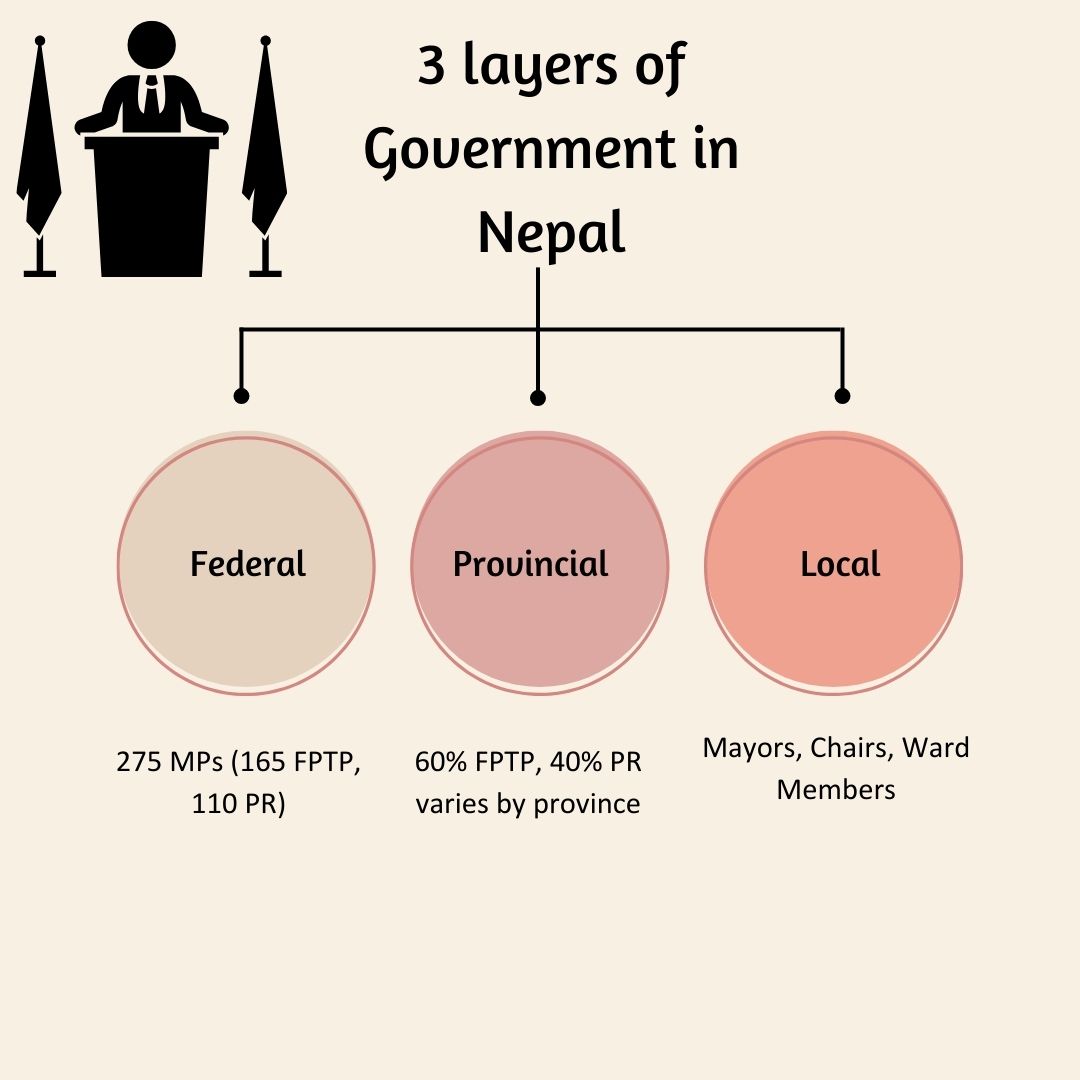
Nepal Government has been restructured into a federal democratic republic since 2015. The constitutional framework establishes three tiers of governance that work collaboratively to serve 29.1 million citizens across 147,516 square kilometers.
The federal system was adopted through the Constitution of Nepal 2015 (2072 BS), moving away from centuries-old centralized governance. This transformation distributes state powers among federal, provincial, and local levels, ensuring inclusive development and regional balance.
Three-Tier Government System in Nepal
Federal Government (Central Level)
Nepal Government at the federal level handles national sovereignty matters. The federal parliament consists of 275 House of Representatives members and 59 National Assembly members. The Prime Minister leads the executive branch.
Key responsibilities include:
- National defense and foreign policy
- Monetary and fiscal policies
- Citizenship laws and immigration
- National highways and infrastructure
- Supreme Court administration
- International trade agreements
Provincial Government (Seven Provinces)
Seven provinces have been established with directly elected leadership. Each province maintains its capital and unicameral legislative assembly. Chief Ministers head provincial governments.
Constitutional powers comprise:
- Provincial law enforcement
- Higher education institutions
- Medium-scale infrastructure projects
- Provincial highway management
- Agricultural development
- Tourism promotion
- Regional economic planning
Local Government (753 Units)
Local level consists of 6 metropolitan cities, 11 sub-metropolitan cities, 276 municipalities, and 460 rural municipalities. Mayors and chairpersons are directly elected by citizens.
Primary functions encompass:
- Primary education and basic healthcare
- Local water supply and sanitation
- Waste management services
- Local road maintenance
- Building permits and zoning
- Birth and death registration
- Local market regulation
Constitutional Powers Distribution
|
Government Level |
Exclusive Powers |
Concurrent Powers |
|
Federal |
35 rights |
25 shared with provinces |
|
Provincial |
21 rights |
15 shared with all levels |
|
Local |
22 rights |
Revenue collection authorized |
Schedule 5, 6, and 8 of the Constitution define exclusive powers. Concurrent powers are outlined in Schedules 7 and 9, requiring coordination among tiers.
31 Fundamental Rights Guaranteed by Nepal Government
The Constitution guarantees comprehensive rights to all citizens:
- Right to live with dignity
- Right to freedom
- Right to equality
- Right to communication
- Right relating to justice
- Right of victim of crime
- Right against torture
- Right against preventive detention
- Right against untouchability and discrimination
- Right relating to property
- Right to freedom of religion
- Right to information
- Right to privacy
- Right against exploitation
- Right to clean environment
- Right to education
- Right to language and culture
- Right to employment
- Right to labor
- Right to health
- Right to food
- Right to shelter
- Right of women
- Right of children
- Right of Dalits
- Right of senior citizens
- Right to social justice
- Right to social security
- Right of consumer
- Right against exile
- Right to constitutional remedies
Citizen Duties Under Nepal Government
Article 48 of the Constitution mandates four fundamental duties:
- Safeguard nationality, sovereignty, and integrity
- Abide by Constitution and laws
- Render compulsory service when required
- Protect and preserve public property
Additional civic responsibilities include tax payment, environmental protection, democratic participation, and social harmony promotion.
Digital Services and Online Portals
Nepal Government has digitized numerous services through dedicated portals:
Essential Citizen Services
- Nepal Government National Portal - Central hub for policies and services
- Nagarik App - Unified mobile service gateway
- Citizen Portal - National ID and civil registration
Taxation and Business Services
- IRD Taxpayer Portal - Tax filing and registration
- OCR Portal - Company registration services
- NNSW Portal - Trade facilitation platform
Travel and Immigration Services
- Immigration Portal - Visa applications
- Passport Portal - Passport services
- Nepal Tourism Board - Tourism information
Inter-Governmental Coordination Mechanisms
Coordination among three tiers is facilitated through:
- National Natural Resources and Fiscal Commission - Revenue distribution
- Inter-State Council - Dispute resolution
- District Coordination Committees - Local-federal liaison
- Provincial Planning Commissions - Development coordination
Recent Developments and Legal Reforms
Nepal Government implemented significant changes in 2025:
- E-filing system introduced in Supreme Court
- Digital Service Tax threshold increased to NPR 3 million
- New IT Bill drafted for enhanced data security
- Climate change legislation proposed through draft bill
Service Delivery Statistics
|
Service Category |
Federal |
Provincial |
Local |
|
Education |
Universities |
Colleges |
Schools |
|
Healthcare |
Specialized hospitals |
Provincial hospitals |
Health posts |
|
Infrastructure |
National highways |
Provincial roads |
Local roads |
|
Revenue Collection |
Customs, income tax |
Vehicle tax, entertainment tax |
Property tax, business tax |
Citizen Participation in Governance
Democratic participation mechanisms include:
- Voting in elections (federal, provincial, local)
- Public hearings on policy matters
- Right to information requests
- Public interest litigation
- Community participation in local development
Challenges and Solutions
Current implementation challenges encompass:
- Coordination gaps among government levels
- Resource constraints at local levels
- Capacity building requirements
- Legal framework harmonization needs
Solutions being implemented:
- Joint training programs for officials
- Integrated planning mechanisms
- Resource sharing protocols
- Digital infrastructure development
International Cooperation and Relations
Nepal Government maintains diplomatic relations with 170+ countries. Key international partnerships include:
- United Nations peacekeeping contributions
- South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC)
- Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC)
- Belt and Road Initiative participation
Future Roadmap and Vision
The 15th Periodic Plan (2024-2029) focuses on:
- Prosperous Nepal, Happy Nepali vision
- Digital governance expansion
- Sustainable development goals
- Inclusive economic growth
- Good governance strengthening
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the structure of Nepal Government?
Nepal Government follows a three-tier federal system with federal, provincial, and local levels established by the 2015 Constitution.
How many provinces are in Nepal?
Seven provinces have been established with their own governments and constitutional powers.
What services does Nepal Government provide online?
Numerous services including tax filing, passport applications, company registration, and citizen ID services through dedicated portals.
What are the fundamental rights in Nepal?
The Constitution guarantees 31 fundamental rights including education, healthcare, equality, and property rights.
How does the federal system work in Nepal?
Power is distributed among three levels with exclusive and concurrent powers defined in constitutional schedules.
What is the role of local government in Nepal?
Local governments handle primary education, basic healthcare, local infrastructure, and citizen services at grassroots level.
How can citizens participate in governance?
Through voting, public hearings, right to information, public interest litigation, and community development programs.
What are the duties of Nepali citizens?
Citizens must safeguard national integrity, abide by laws, render service when required, and protect public property.
How is revenue distributed among government levels?
Through the National Natural Resources and Fiscal Commission based on constitutional provisions.
What recent reforms have been implemented?
Digital transformation initiatives, tax reforms, e-governance expansion, and legal framework updates in 2024.
Government portal of Nepal
- Constitution of Nepal 2015 - Official constitutional document
- Nepal Government National Portal - Official government information
- Federal Parliament of Nepal - Legislative information
- Local Government Operation Act, 2074 - Legal framework for local governance
- National Natural Resources and Fiscal Commission - Inter-governmental fiscal arrangements
- Nepal Law Commission - Legal database and updates
- Office of the Prime Minister - Executive branch information
- Election Commission Nepal - Democratic process information
Contact Nepal Government Services: nepal.gov.np
Legal Disclaimer: This guide provides general information about Nepal Government structure and services. For specific legal matters, consult authorized government officials or legal practitioners.